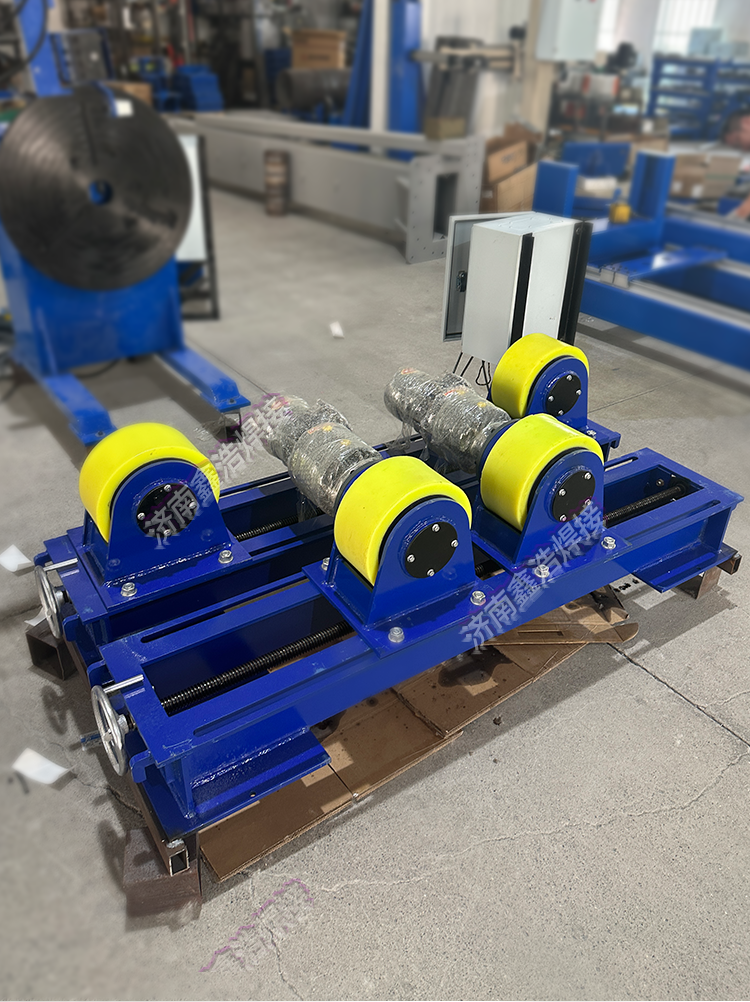
- Pressure Vessel and Special Equipment Manufacturing Industry
This represents the most critical application area for welding turning rolls. The industry requires exceptionally high welding quality—particularly in terms of sealing and pressure resistance—and often deals with large-diameter, heavy cylindrical or spherical structures. Stable rotational movement during welding is essential and achievable only with turning rolls.
Typical Workpieces:
Pressure vessels (e.g., reactors, storage tanks, heat exchangers, boiler drums);
Special equipment (e.g., liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage tanks, hydrogen storage tanks, medical high-pressure sterilizers).
Application Logic:
These workpieces typically measure from 1 meter to several meters in diameter and can weigh tens of tons, making manual rotation impractical. Welding turning rolls adjust to varying diameters through customizable roller spacing, provide precise rotation speed control (synchronized with welding current and wire feed speed), and ensure uniform circumferential welding. This minimizes defects such as lack of fusion or porosity caused by workpiece misalignment.
- Petrochemical and Oil & Gas Transmission Industry
The petrochemical sector relies heavily on pipelines and storage equipment, which often consist of long, thick-walled pipes or large tanks. Welding turning rolls are vital for efficient batch welding operations.
Typical Workpieces:
Oil and gas transmission pipelines (e.g., spiral welded pipes for long-distance lines, longitudinal submerged arc welded pipes);
Chemical storage tanks (e.g., crude oil tanks, methanol tanks, acid-alkaline solution tanks);
Refining equipment (e.g., cylindrical sections of towers and reactors).
Application Logic:
Pipeline segments often measure 10–12 meters in length with diameters between 0.5–2 meters, requiring circumferential welding for assembly. Large storage tanks frequently exceed 20 meters in diameter and are constructed from rolled and welded steel plates. Turning rolls provide stable support and 360° rotation, enabling continuous welding processes such as submerged arc or gas-shielded welding. This improves construction efficiency by 3–5 times compared to manual turning.
- Construction Machinery and Heavy Equipment Manufacturing Industry
This industry regularly produces rotating or cylindrical components—such as hydraulic cylinders, track frames, and drums—that require precise and efficient welding.
Typical Workpieces:
Hydraulic cylinder barrels, crane drums (for wire winding);
Excavator track frames (including cylindrical supports), loader bucket cylinders;
Drive shaft sleeves for heavy trucks, slewing bearing rings for construction machinery.
Application Logic:
Workpieces generally range from 0.1–1 meter in diameter and weigh a few tons or less, but are produced in high volumes. Compact, adjustable welding turning rolls allow rapid switching between workpiece sizes, combine rotation with automated wire feeding, reduce human error, and significantly increase output—for example, enabling daily production of hundreds of cylinder barrels.
- Wind Power and New Energy Equipment Manufacturing Industry
Key components like tower sections and flanges in wind energy systems are large cylindrical structures that demand heavy-duty welding support.
Typical Workpieces:
Wind tower segments (typically 3–5 meters in diameter, 10–15 meters long, weighing 30–50 tons each);
Tower flanges (annular parts welded to tower segments, with thicknesses of 50–100 mm);
Large steel tubes for photovoltaic mounting systems, cylindrical energy storage containers.
Application Logic:
Wind tower manufacturing requires high-precision longitudinal and circumferential welding capable of enduring long-term vibrational stress. Large self-adjusting or hydraulic turning rolls offer stable support for ultra-heavy components, with servo-controlled rotation speeds as precise as 0.1 r/min. This ensures optimal synchronization with welding parameters, preventing defects such as lack of penetration or stress concentration.
- Shipbuilding and Offshore Engineering Industry
Ships and offshore structures incorporate numerous cylindrical elements such as pipes, tanks, and pile legs. Turning rolls are especially useful for prefabrication and circumferential welding.
Typical Workpieces:
Ship piping systems (e.g., fuel, cooling water, and ballast pipes, with diameters of 20–500 mm);
Offshore platform pile legs (cylindrical or conical tubes, 1–3 meters in diameter);
Cylindrical sections of ballast and fuel tanks.
Application Logic:
Pipe networks are often prefabricated in workshops using turning rolls that provide 360° rotation and variable speed, enabling automatic welding and reducing onsite labor. This improves welding efficiency by 2–3 times. Long pile legs are welded in segments, with turning rolls supporting and rotating each section for all-position welding access.
- Steel Structure and General Machinery Manufacturing Industry
Cylindrical parts used in structural and mechanical applications—such as columns, housings, and sleeves—benefit from the use of turning rolls even in smaller-scale production.
Typical Workpieces:
Large-diameter steel pipes (e.g., factory columns, bridge arch ribs, 0.5–2 meters in diameter);
Machinery housings (e.g., centrifugal fan casings, pump bodies);
Cylindrical outer bearing sleeves.
Application Logic:
These applications typically involve single or small-batch production, requiring flexible and easy-to-use equipment. Light-duty, manually adjustable turning rolls offer quick setup and adaptability without complex controls, mainly reducing physical effort and simplifying the welding of cylindrical parts.
Summary: Core Application Scenarios for Welding Turning Rolls
In summary, welding turning rolls address the need for rotating cylindrical and similarly shaped workpieces during welding. Their use is determined by two main factors:
- Workpiece shape: cylindrical, tubular, or annular forms;
- Welding requirements: batch production, high precision, or size/weight beyond manual capacity.
While other industries—such as mining (e.g., conveyor drums) and aerospace (e.g., small cylinder welding)—also use turning rolls, their adoption is less frequent and narrower in scope compared to the six major sectors listed above.