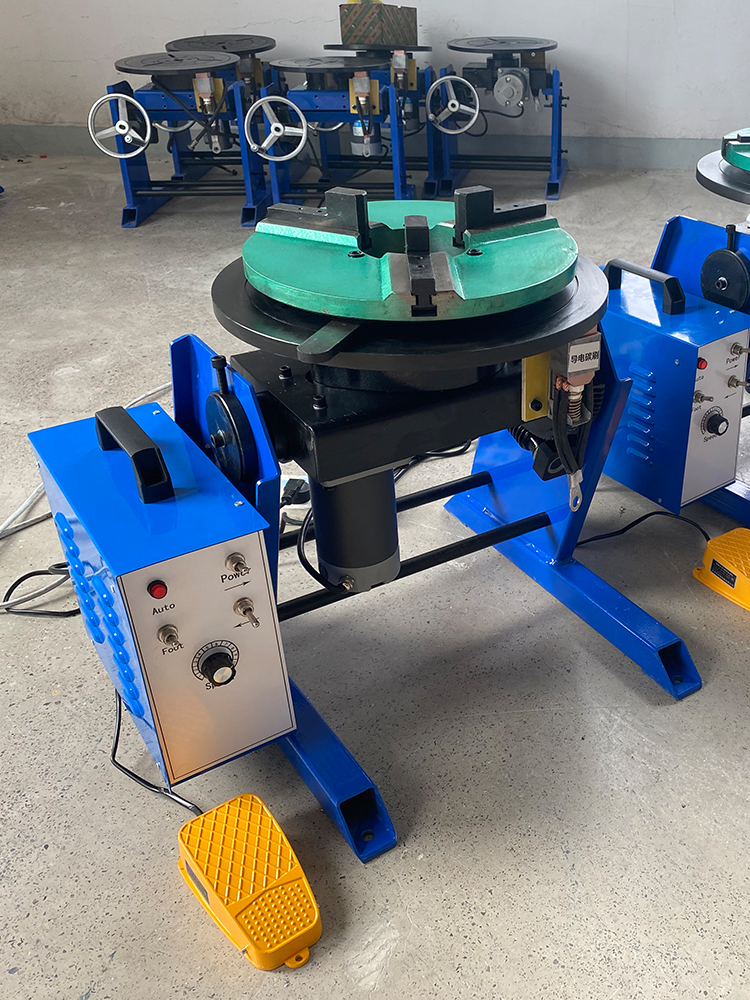
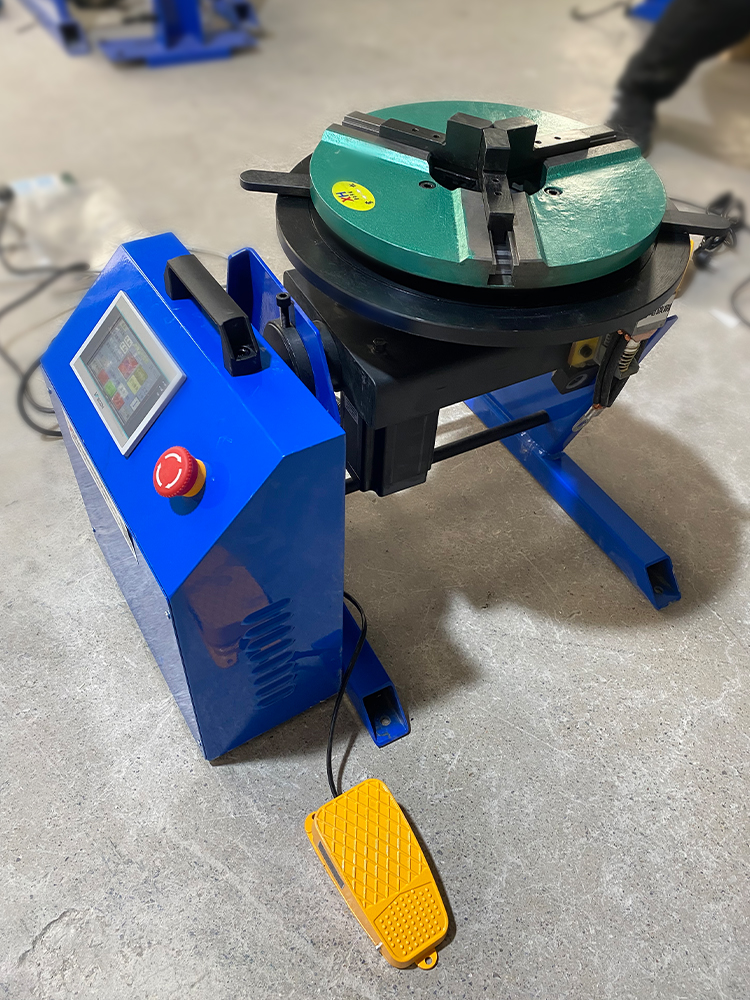
I. Tägliche Wartung (vor und nach dem täglichen Betrieb)
Reinigung und Inspektion
- Entfernen Sie Schweißschlacke, Spritzer, Ölflecken und Staub von der Oberfläche des Geräts, insbesondere von wichtigen Teilen wie dem Drehmechanismus und den Führungsschienen, um zu verhindern, dass sich Schlacken festsetzen und die Bewegungsgenauigkeit beeinträchtigen.
- Überprüfen Sie, ob Kabel und Luftleitungen beschädigt oder gealtert sind und ob die Verbindungen locker sind, um eine normale Strom- und Luftzufuhr zu gewährleisten.
Inspektion von beweglichen Teilen
- Beobachten Sie, ob die Bewegung jeder rotierenden Welle und jedes Drehmechanismus stabil ist und ob es anormale Geräusche, Blockierungen oder Abweichungen gibt.
- Prüfen Sie, ob die Grenzwertgeber (z. B. Wegschalter, Lichtschranken) empfindlich und zuverlässig sind, um Schäden an der Anlage durch Überfahren des Weges zu vermeiden.
Schmierung Ergänzung
- Fügen Sie den Reibungsteilen wie Lagern, Zahnrädern und Führungsschienen gemäß den Anweisungen Schmieröl oder -fett (z. B. Butter, Maschinenöl) hinzu, um eine reibungslose Bewegung zu gewährleisten und den Verschleiß zu verringern.
II. Regelmäßige Wartung (wöchentlich / monatlich / vierteljährlich, je nach Nutzungshäufigkeit)
Wartung der mechanischen Struktur
- Befestigungsteile: Prüfen Sie, ob Verbindungselemente wie Schrauben, Muttern und Stifte locker sind, insbesondere die Teile, die während des Schweißens Vibrationen ausgesetzt sind (z. B. die Verbindung zwischen der Werkbank und dem rotierenden Körper, der Motorbefestigungssitz), und ziehen Sie sie rechtzeitig fest.
- Wartung von Zahnrädern und Ketten: Wenn das Gerät über ein Getriebe oder eine Kette verfügt, müssen die Ablagerungen zwischen den Zähnen oder Kettengliedern regelmäßig gereinigt, die Abnutzung der Zahnoberflächen und die Dichtheit der Ketten überprüft und die Spannvorrichtung eingestellt oder Ersatzteile ausgetauscht werden, falls erforderlich.
- Wartung der Führungsschienen: Wischen Sie die Oberfläche der Führungsschienen ab und tragen Sie Rostschutzöl auf, um Rost zu vermeiden; überprüfen Sie die Parallelität und Geradheit der Führungsschienen und stellen Sie sie rechtzeitig ein, wenn es Abweichungen gibt.
Wartung des Antriebssystems
- Überprüfung des Motors: Reinigen Sie die Oberfläche des Motors, prüfen Sie, ob die Klemmenblöcke überhitzt oder oxidiert sind und ob die Lager anormale Geräusche aufweisen; messen Sie den Isolationswiderstand des Motors, um sicherzustellen, dass er den Sicherheitsstandards entspricht (im Allgemeinen ≥0,5 MΩ).
- Wartung des Getriebes: Prüfen Sie den Ölstand des Getriebes und fügen Sie dieselbe Art von Getriebeöl hinzu, wenn er nicht ausreicht; wenn ein Ölaustritt festgestellt wird, ersetzen Sie die Dichtungen (z. B. Öldichtungen) rechtzeitig und reinigen Sie die ausgelaufenen Ölflecken.
Wartung des elektrischen Systems
- Öffnen Sie den elektrischen Schaltschrank, entfernen Sie Staub und Schmutz aus dem Inneren, prüfen Sie, ob die Kontakte der Schütze und Relais abgetragen sind, und schleifen Sie sie ab oder tauschen Sie sie rechtzeitig aus, wenn sie abgenutzt sind.
- Prüfen Sie, ob die Verdrahtung von Steuerungskomponenten wie SPS und Servoantrieben fest ist, ob die Kontrollleuchten normal leuchten und ermitteln Sie gegebenenfalls deren Betriebsparameter mit Spezialgeräten.
Wartung des hydraulischen / pneumatischen Systems (für Stellungsregler mit hydraulischem / pneumatischem Antrieb)
- Hydraulisches System: Prüfen Sie den Ölstand im Öltank, wechseln Sie das Hydrauliköl regelmäßig aus (in der Regel alle 6-12 Monate) und reinigen Sie den Filter; prüfen Sie, ob die Ölleitungen und Hydraulikventile undicht sind und ob sich der Ölzylinder leichtgängig bewegt, und tauschen Sie gegebenenfalls die Dichtungen aus.
- Pneumatisches System: Wasser ablassen (das Ablassventil des Luftspeichers oder des Filters öffnen, um das Kondenswasser abzulassen); den Arbeitsstatus des Druckminderers und des Magnetventils überprüfen und die Verunreinigungen in den pneumatischen Komponenten reinigen, um eine Blockierung des Luftkreislaufs zu verhindern.
III. Wartung bei langfristiger Abschaltung
Wenn das Gerät für eine längere Zeit (mehr als 1 Monat) abgeschaltet werden muss, sollten folgende Arbeiten durchgeführt werden:
- Reinigen Sie die Oberfläche und das Innere des Geräts gründlich und tragen Sie Rostschutzfarbe oder Rostschutzöl auf alle freiliegenden Metallteile auf.
- Bringen Sie jede bewegliche Achse in die "Nullposition" oder in eine sichere Position, um eine Verformung der Teile durch Krafteinwirkung zu vermeiden.
- Trennen Sie die Stromversorgung und die Luftquelle, entfernen Sie die Kabel und Luftleitungen und lagern Sie sie ordnungsgemäß, und legen Sie Trockenmittel in den Schaltschrank, um Feuchtigkeit zu vermeiden.
- Decken Sie das Gerät mit einer Staubschutzhaube ab, um das Eindringen von Staub und Schmutz in das Gerät zu verhindern.
IV. Umgang mit allgemeinen Fehlern und Vorsichtsmaßnahmen
- Grundsätze für die Fehlerbehebung: Wenn eine abnormale Ausrüstung festgestellt wird, muss die Maschine sofort für eine Inspektion gestoppt werden, und es ist verboten, mit Störungen zu arbeiten; einfache Störungen (z. B. Lockerheit, Ölmangel) können selbst behoben werden, und komplexe Störungen (z. B. Motordurchbrennen, Ausfall des Steuersystems) müssen von professionellem Wartungspersonal behoben werden.
- Sicherheitsvorkehrungen: Bei Wartungsarbeiten muss die Stromversorgung unterbrochen und ein Schild "Einschalten verboten" aufgehängt werden; bei Arbeiten in großer Höhe (z. B. Überprüfung der Oberseite des Drehmechanismus) müssen Sicherheitsgurte angelegt werden; bei der Verwendung von brennbaren Stoffen wie Schmieröl und Reinigungsmitteln ist ein Abstand zu Brandquellen einzuhalten.