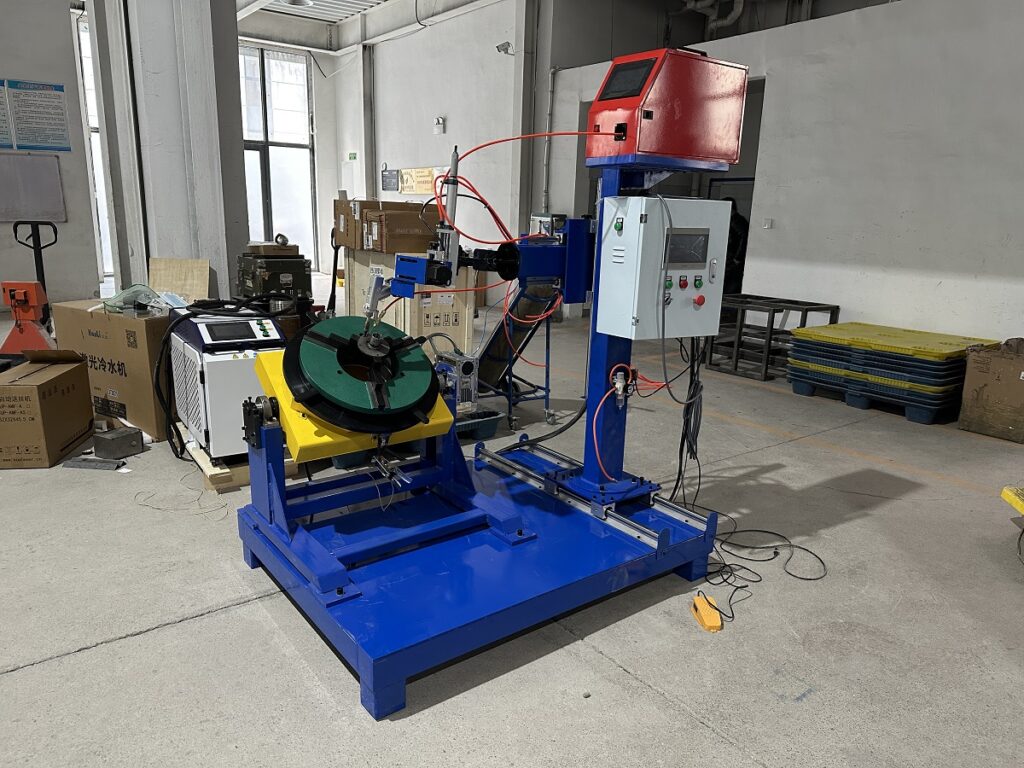
Key Considerations for Laser Automatic Welding
Laser automatic welding is a highly efficient and precise technology widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. To ensure optimal performance, safety, and weld quality, here are some essential considerations:
1. Laser Safety Precautions
- Always wear appropriate laser safety goggles to protect eyes from harmful radiation.
- Ensure the work area is enclosed with protective barriers to prevent accidental exposure.
- Follow OSHA and ANSI Z136.1 standards for laser operation.
2. Material Compatibility
- Verify that the materials being welded (e.g., steel, aluminum, titanium) are suitable for laser welding.
- Some metals may require preheating or shielding gas (e.g., argon, helium) to prevent oxidation.
3. Machine Calibration & Maintenance
- Regularly calibrate the laser beam alignment to maintain precision.
- Clean the focusing lens and mirrors to avoid energy loss and defects.
- Monitor cooling systems to prevent overheating.
4. Optimal Welding Parameters
- Adjust power, speed, and pulse frequency based on material thickness and type.
- Conduct test welds to fine-tune settings before full-scale production.
5. Joint Preparation & Fit-Up
- Ensure tight joint fit-up with minimal gaps for high-quality welds.
- Remove contaminants like oil, rust, or coatings that may affect weld integrity.
6. Real-Time Monitoring & Quality Control
- Use sensors and cameras to detect defects (e.g., porosity, cracks) during welding.
- Implement automated inspection systems for consistent quality assurance.
7. Ventilation & Fume Extraction
- Laser welding can produce hazardous fumes—install local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems.